|
Mobile terminal (portable data terminal)
Modern technologies allow trade and warehouse inventory management to
be automated. Due to automation, personnel load can be considerably
reduced, and even one person can perform the inventory of thousands of
items and draw up all the necessary documents with relative ease.
The portable data terminal allows data about items to be acquired and
transferred to the companyТs database. The specifics of the operation of
secure storage warehousing businesses, in which the flow of items is
constant and needs real-time control, implies continuous connection with
the companyТs database and instant transfer of information about the
registered flows of items to the database.
The mobile terminal allows the following types of items to be
processed:
1. Items with individual or serial barcodes.
2. Items without barcodes identifiable by stock numbers or item names.
There is an option of entering the data concerning a new item directly
from the mobile terminal; in such case the label will be printed on the
portable printer.
3. Master-boxes with varying quantities in the box.
4. Piece items identifiable by serial numbers in the barcode.
5. Items with weight barcodes.
6. Unidentified items which are marked with bin locations until they
have been identified and sorted.
Incoming items are generally processes as marked, unmarked and not
subject to marking. If the incoming marking is not sufficiently
informative, it can be replaced or supplemented with the warehouseТs
marking.
He mobile terminal has the following functions:
TRANSFER OF TASKS B/N OFFICE AND WAREHOUSE, WORK MONITORING Ц
separate task lists for pre-scheduled receipt, detailed receipt,
pre-scheduled pick-up, issue and loading to the vehicle. In the form of
prominent colour-coded indication blinking in red and the number of the
documents forwarded to the warehouse on each list.
UNLOADING Ц the transfer of the items that have arrived from
the medium of transportation to the sorting area.
DETAILED RECEIPT Ц the sorting of the items that have arrived
and their placement in storage bins.
PRELIM. PICK-UP Ц the pre-scheduled pick-up for issuing or
consolidation of the items ordered on pallets without writing them off
the warehouse inventory for placement in the pick-up and issue area.
PICK-UP FOR ISSUE Ц direct issue from the warehouse upon the
customerТs order, with consolidation during the pick-up, on pallets or
without them.
LOAD FROM PALLETS Ц the issue of the items assembled on
pallets with an option of checking that the pick-up has been correct.
ISSUE ON PALLET CHECKING Ц the mode for checking that the
pick-up of items on pallets has been correct.
INVENTORY Ц an optional mode to be set up for each customer
separately in accordance with the peculiarities of the turnover in
addition to taking inventory of the pallet and the bin,
PALLET RELOCATION Ц the relocation of an individual pallet,
including the relocation initiated by a warehouse employee, for the
purpose of cargo placement optimization or pre-scheduled relocation for
pick-up without changing the documented status of the items.
BOX RELOCATION Ц the relocation of an item of goods, including
the relocation initiated by a warehouse employee, for the purpose of
cargo placement optimization or pre-scheduled relocation for pick-up
without changing the documented status of the items.
NEW PALLET Ц the creation of a new pallet number with the
option of printing the pallet sticker on the portable printer. There is
also an option of bulk printing of labels with consecutive numbers and
with the register of numbers in order to prevent the duplication of
pallet numbers.
NEW BOX Ц the creation of a new box number or piece item with
the option of printing the sticker on the portable printer. There is
also an option of bulk printing of labels with consecutive numbers and
with the register of numbers in order to prevent the duplication of box
numbers.
CREATE PALLET ITEM CARD Ц the creation of a new item card in
the course of item identification. There is an option of printing
stickers for boxes or piece items from the form of data entry of the
item card.
IDENTIFY ITEM Ц identifying the name and other item attributes
by means of the barcode.
BIN CONTENT Ц taking inventory of the items in the bin.
PALLET CONTENT Ц taking inventory of the items on the pallet.
PUT BIN ON PALLET Ц a service mode assisting in the initial
location of items in bin locations and in the replacement of pallets /
pallet stickers.
A bin location warehousing module has been integrated in the
WMS.Management software package. The user can receive information about
stock balance and the actual location where the items are stored at any
moment, including the precise specification down to the end bin. The
implementation of bin location warehousing technology is necessary so
that the storage of items can be streamlined, stock optimization methods
can be devised and interwarehouse hauling can be reduced. The bin
location warehousing technology is based on barcoding and is organized
by means of numbering the bins, pallets, items, etc.
The office-installed part of the bin location warehousing module, which
is used as the basis for operating the mobile terminal, features options
for viewing and correcting data as well as printing out documents
concerning the status of the cargo on the basis of its physical
location. The reporting system allows the status of the item to be
viewed in real time, on a particular date, and on the basis of arrival
and issue turnover broken down by the following attributes: the
warehouse (physical or customs warehouse), customer, document, order
number, stock number, name, number of the container or transportation
unit, bin number, piece barcode, pallet barcode, number of the physical
operation, etc.
The bin location warehousing module and the mobile terminals
connected to it work around the problem which arises when it is
impossible to pick up or place the cargo and to make changes to its
documentation at the same time. Now the cargo can be warehoused upon
arrival or picked up before dispatch while it is simultaneously getting
customs clearance, because information is available in two databases:
the data concerning documents and the data concerning the physical
location.
The interface of the software can be provided in any language
depending on the customerТs preferences (Estonian, Russian, English,
Latvian, etc.).
ќсновное меню мобильного терминала
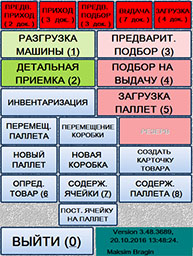
|
ѕул (список) задач по приему
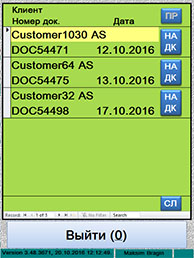
|
ƒокумент по приему
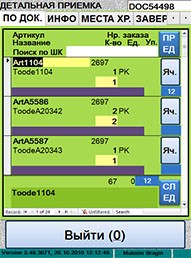
|
ќбща€ информаци€ о приеме
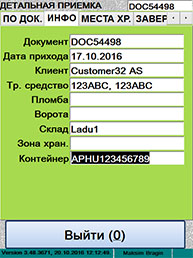
|
|
–егистраци€ товара при детальной
приемке
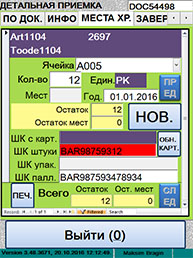
|
–егистраци€ окончани€ детальной
приемки

|
ѕодпись при
окончании детальной приемки

|
| —писок товара дл€ предварительного
подбора
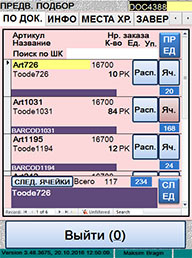
|
–егистраци€ подобранного
товара при предварительном подборе
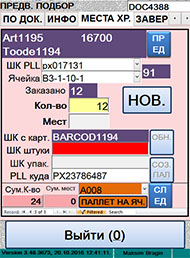
|
»нформаци€ о расположении товара
дл€ подбора
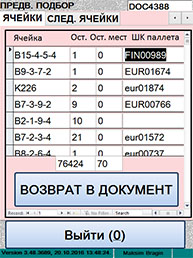
|
ƒетальные указани€ программного
комплекса по подбору товара
с €чеек
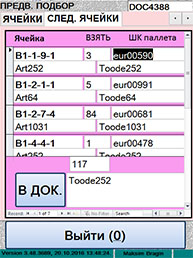
|
| ѕерестановка коробок
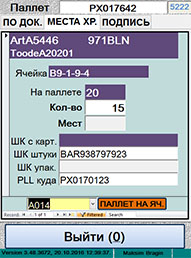 |
ѕерестановка паллета
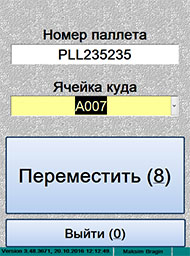 |
ѕечать этикеток дл€ паллет
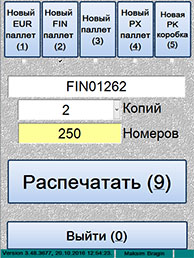 |

|







